ODEs Subpackage¶
Inheritance Diagram¶
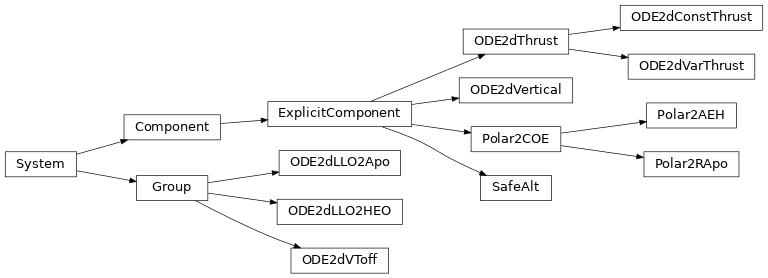
Modules List¶
@authors: Alberto FOSSA’ Giuliana Elena MICELI |
|
@authors: Alberto FOSSA’ Giuliana Elena MICELI |
Documentation¶
@authors: Alberto FOSSA’ Giuliana Elena MICELI
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d.ODE2dThrust(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
openmdao.core.explicitcomponent.ExplicitComponentODE2dThrust class defines the equations of motion for a two dim. powered trajectory.
- Other Parameters
time (ndarray) – Represents the time variable of the system [-]
r (ndarray) – Represents a position along the trajectory. The distance is measured from the center of the central body [-]
theta (ndarray) – Angle spawn from the starting point of the orbit to the final one [-]
u (ndarray) – Radial velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
v (ndarray) – Tangential velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
m (ndarray) – Mass of the space vehicle that performs the trajectory [-]
alpha (ndarray) – Angle defining the thrust direction [-]
thrust (ndarray) – Value of the applied thrust force [-]
w (float) – Value of the exhaust velocity [-]
num_nodes (int) – Number of nodes where to compute the equations
GM (float) – Standard gravitational parameter for the central attracting body [-]
-
initialize()[source] Initializes the ODE2dThrust class variables.
-
setup()[source] Setup of ODE2dThrust parameters. Declaration of input, output and partials variables.
-
compute(inputs, outputs)[source] Compute the output variables.
-
compute_partials(inputs, jacobian)[source] Compute the partial derivatives variables.
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_discrete_input(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add a discrete input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_discrete_output(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
tags (str or list of strs or set of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_input(name, val=1.0, shape=None, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None, units=None, desc='', tags=None) Add an input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray or Iterable) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if src_indices not provided and val is not an array. Default is None.
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. A value of None implies this input depends on all entries of source. Default is None. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise each entry must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
units (str or None) – Units in which this input variable will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it is unitless.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_output(name, val=1.0, shape=None, units=None, res_units=None, desc='', lower=None, upper=None, ref=1.0, ref0=0.0, res_ref=None, tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
For ExplicitComponent, res_ref defaults to the value in res unless otherwise specified.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if val is not an array. Default is None.
units (str or None) – Units in which the output variables will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it has no units.
res_units (str or None) – Units in which the residuals of this output will be given to the user when requested. Default is None, which means it has no units.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
lower (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – lower bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no lower bound. Default is None.
upper (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – upper bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no upper bound. Default is None.
ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 1. Default is 1.
ref0 (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 0. Default is 0.
res_ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined res_units of this output’s residual when the scaled value is 1. Default is None, which means residual scaling matches output scaling.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs and also when listing results from case recorders.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute_jacvec_product(inputs, d_inputs, d_outputs, mode, discrete_inputs=None) Compute jac-vector product. The model is assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- If mode is:
‘fwd’: d_inputs |-> d_outputs
‘rev’: d_outputs |-> d_inputs
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
d_inputs (Vector) – see inputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_inputs
d_outputs (Vector) – see outputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_outputs
mode (str) – either ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
declare_partials(of, wrt, dependent=True, rows=None, cols=None, val=None, method='exact', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Declare information about this component’s subjacobians.
- Parameters
of (str or list of str) – The name of the residual(s) that derivatives are being computed for. May also contain a glob pattern.
wrt (str or list of str) – The name of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
dependent (bool(True)) – If False, specifies no dependence between the output(s) and the input(s). This is only necessary in the case of a sparse global jacobian, because if ‘dependent=False’ is not specified and declare_partials is not called for a given pair, then a dense matrix of zeros will be allocated in the sparse global jacobian for that pair. In the case of a dense global jacobian it doesn’t matter because the space for a dense subjac will always be allocated for every pair.
rows (ndarray of int or None) – Row indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
cols (ndarray of int or None) – Column indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
val (float or ndarray of float or scipy.sparse) – Value of subjacobian. If rows and cols are not None, this will contain the values found at each (row, col) location in the subjac.
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step, ‘exact’: use the component defined analytic derivatives. Default is ‘exact’.
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
- Returns
Metadata dict for the specified partial(s).
- Return type
dict
-
property
distributed Provide ‘distributed’ property for backwards compatibility.
- Returns
reference to the ‘distributed’ option.
- Return type
bool
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
ode_options= <dymos.ode_options.ODEOptions object>
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_check_partial_options(wrt, method='fd', form=None, step=None, step_calc=None, directional=False) Set options that will be used for checking partial derivatives.
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
method (str) – Method for check: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form for check, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference check. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step_calc (str) – Type of step calculation for check, can be “abs” for absolute (default) or “rel” for relative. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
directional (bool) – Set to True to perform a single directional derivative for each vector variable in the pattern named in wrt.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d.ODE2dConstThrust(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
latom.odes.odes_2d.ODE2dThrustODE2dConstThrust class defines the equations of motion for a two dim. powered trajectory with constant thrust.
- Other Parameters
time (ndarray) – Represents the time variable of the system [-]
r (ndarray) – Represents a position along the trajectory. The distance is measured from the center of the central body [-]
theta (ndarray) – Angle spawn from the starting point of the orbit to the final one [-]
u (ndarray) – Radial velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
v (ndarray) – Tangential velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
m (ndarray) – Mass of the space vehicle that performs the trajectory [-]
alpha (ndarray) – Angle defining the thrust direction [-]
thrust (ndarray) – Value of the applied thrust force [-]
w (float) – Value of the exhaust velocity [-]
num_nodes (int) – Number of nodes where to compute the equations
GM (float) – Standard gravitational parameter for the central attracting body [-]
T (float) – Value of the constant thrust force [-]
-
initialize()[source] Initializes the ODE2dConstThrust class variables.
-
setup()[source] Setup of ODE2dConstThrust parameters. Declaration of input, output and partials variables.
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_discrete_input(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add a discrete input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_discrete_output(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
tags (str or list of strs or set of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_input(name, val=1.0, shape=None, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None, units=None, desc='', tags=None) Add an input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray or Iterable) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if src_indices not provided and val is not an array. Default is None.
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. A value of None implies this input depends on all entries of source. Default is None. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise each entry must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
units (str or None) – Units in which this input variable will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it is unitless.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_output(name, val=1.0, shape=None, units=None, res_units=None, desc='', lower=None, upper=None, ref=1.0, ref0=0.0, res_ref=None, tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
For ExplicitComponent, res_ref defaults to the value in res unless otherwise specified.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if val is not an array. Default is None.
units (str or None) – Units in which the output variables will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it has no units.
res_units (str or None) – Units in which the residuals of this output will be given to the user when requested. Default is None, which means it has no units.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
lower (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – lower bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no lower bound. Default is None.
upper (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – upper bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no upper bound. Default is None.
ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 1. Default is 1.
ref0 (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 0. Default is 0.
res_ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined res_units of this output’s residual when the scaled value is 1. Default is None, which means residual scaling matches output scaling.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs and also when listing results from case recorders.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute(inputs, outputs) Compute the output variables.
-
compute_jacvec_product(inputs, d_inputs, d_outputs, mode, discrete_inputs=None) Compute jac-vector product. The model is assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- If mode is:
‘fwd’: d_inputs |-> d_outputs
‘rev’: d_outputs |-> d_inputs
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
d_inputs (Vector) – see inputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_inputs
d_outputs (Vector) – see outputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_outputs
mode (str) – either ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
-
compute_partials(inputs, jacobian) Compute the partial derivatives variables.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
declare_partials(of, wrt, dependent=True, rows=None, cols=None, val=None, method='exact', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Declare information about this component’s subjacobians.
- Parameters
of (str or list of str) – The name of the residual(s) that derivatives are being computed for. May also contain a glob pattern.
wrt (str or list of str) – The name of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
dependent (bool(True)) – If False, specifies no dependence between the output(s) and the input(s). This is only necessary in the case of a sparse global jacobian, because if ‘dependent=False’ is not specified and declare_partials is not called for a given pair, then a dense matrix of zeros will be allocated in the sparse global jacobian for that pair. In the case of a dense global jacobian it doesn’t matter because the space for a dense subjac will always be allocated for every pair.
rows (ndarray of int or None) – Row indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
cols (ndarray of int or None) – Column indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
val (float or ndarray of float or scipy.sparse) – Value of subjacobian. If rows and cols are not None, this will contain the values found at each (row, col) location in the subjac.
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step, ‘exact’: use the component defined analytic derivatives. Default is ‘exact’.
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
- Returns
Metadata dict for the specified partial(s).
- Return type
dict
-
property
distributed Provide ‘distributed’ property for backwards compatibility.
- Returns
reference to the ‘distributed’ option.
- Return type
bool
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
ode_options= <dymos.ode_options.ODEOptions object>
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_check_partial_options(wrt, method='fd', form=None, step=None, step_calc=None, directional=False) Set options that will be used for checking partial derivatives.
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
method (str) – Method for check: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form for check, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference check. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step_calc (str) – Type of step calculation for check, can be “abs” for absolute (default) or “rel” for relative. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
directional (bool) – Set to True to perform a single directional derivative for each vector variable in the pattern named in wrt.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d.ODE2dVarThrust(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
latom.odes.odes_2d.ODE2dThrustODE2dVarThrust class defines the equations of motion for a two dim. powered trajectory with variable thrust.
- Other Parameters
time (ndarray) – Represents the time variable of the system [-]
r (ndarray) – Represents a position along the trajectory. The distance is measured from the center of the central body [-]
theta (ndarray) – Angle spawn from the starting point of the orbit to the final one [-]
u (ndarray) – Radial velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
v (ndarray) – Tangential velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
m (ndarray) – Mass of the space vehicle that performs the trajectory [-]
alpha (ndarray) – Angle defining the thrust direction [-]
thrust (ndarray) – Value of the applied thrust force [-]
w (float) – Value of the exhaust velocity [-]
num_nodes (int) – Number of nodes where to compute the equations
GM (float) – Standard gravitational parameter for the central attracting body [-]
-
setup()[source] Setup of ODE2dVarThrust parameters. Declaration of input, output and partials variables.
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_discrete_input(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add a discrete input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_discrete_output(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
tags (str or list of strs or set of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_input(name, val=1.0, shape=None, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None, units=None, desc='', tags=None) Add an input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray or Iterable) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if src_indices not provided and val is not an array. Default is None.
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. A value of None implies this input depends on all entries of source. Default is None. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise each entry must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
units (str or None) – Units in which this input variable will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it is unitless.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_output(name, val=1.0, shape=None, units=None, res_units=None, desc='', lower=None, upper=None, ref=1.0, ref0=0.0, res_ref=None, tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
For ExplicitComponent, res_ref defaults to the value in res unless otherwise specified.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if val is not an array. Default is None.
units (str or None) – Units in which the output variables will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it has no units.
res_units (str or None) – Units in which the residuals of this output will be given to the user when requested. Default is None, which means it has no units.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
lower (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – lower bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no lower bound. Default is None.
upper (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – upper bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no upper bound. Default is None.
ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 1. Default is 1.
ref0 (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 0. Default is 0.
res_ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined res_units of this output’s residual when the scaled value is 1. Default is None, which means residual scaling matches output scaling.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs and also when listing results from case recorders.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute(inputs, outputs) Compute the output variables.
-
compute_jacvec_product(inputs, d_inputs, d_outputs, mode, discrete_inputs=None) Compute jac-vector product. The model is assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- If mode is:
‘fwd’: d_inputs |-> d_outputs
‘rev’: d_outputs |-> d_inputs
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
d_inputs (Vector) – see inputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_inputs
d_outputs (Vector) – see outputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_outputs
mode (str) – either ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
-
compute_partials(inputs, jacobian) Compute the partial derivatives variables.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
declare_partials(of, wrt, dependent=True, rows=None, cols=None, val=None, method='exact', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Declare information about this component’s subjacobians.
- Parameters
of (str or list of str) – The name of the residual(s) that derivatives are being computed for. May also contain a glob pattern.
wrt (str or list of str) – The name of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
dependent (bool(True)) – If False, specifies no dependence between the output(s) and the input(s). This is only necessary in the case of a sparse global jacobian, because if ‘dependent=False’ is not specified and declare_partials is not called for a given pair, then a dense matrix of zeros will be allocated in the sparse global jacobian for that pair. In the case of a dense global jacobian it doesn’t matter because the space for a dense subjac will always be allocated for every pair.
rows (ndarray of int or None) – Row indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
cols (ndarray of int or None) – Column indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
val (float or ndarray of float or scipy.sparse) – Value of subjacobian. If rows and cols are not None, this will contain the values found at each (row, col) location in the subjac.
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step, ‘exact’: use the component defined analytic derivatives. Default is ‘exact’.
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
- Returns
Metadata dict for the specified partial(s).
- Return type
dict
-
property
distributed Provide ‘distributed’ property for backwards compatibility.
- Returns
reference to the ‘distributed’ option.
- Return type
bool
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
initialize() Initializes the ODE2dThrust class variables.
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
ode_options= <dymos.ode_options.ODEOptions object>
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_check_partial_options(wrt, method='fd', form=None, step=None, step_calc=None, directional=False) Set options that will be used for checking partial derivatives.
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
method (str) – Method for check: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form for check, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference check. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step_calc (str) – Type of step calculation for check, can be “abs” for absolute (default) or “rel” for relative. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
directional (bool) – Set to True to perform a single directional derivative for each vector variable in the pattern named in wrt.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d.ODE2dVertical(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
openmdao.core.explicitcomponent.ExplicitComponentODE2dVertical class defines the equations of motion for a two dim. powered trajectory with variable thrust.
- Other Parameters
time (ndarray) – Represents the time variable of the system [-]
r (ndarray) – Represents a position along the trajectory. The distance is measured from the center of the central body [-]
u (ndarray) – Radial velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
m (ndarray) – Mass of the space vehicle that performs the trajectory [-]
thrust (ndarray) – Value of the applied thrust force [-]
w (float) – Value of the exhaust velocity [-]
num_nodes (int) – Number of nodes where to compute the equations
GM (float) – Standard gravitational parameter for the central attracting body [-]
T (float) – Value of the constant thrust force [-]
-
initialize()[source] Initializes the ODE2dVertical class variables.
-
setup()[source] Setup of ODE2dVertical parameters. Declaration of input, output and partials variables.
-
compute(inputs, outputs)[source] Compute the output variables.
-
compute_partials(inputs, jacobian)[source] Compute the partial derivative variables.
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_discrete_input(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add a discrete input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_discrete_output(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
tags (str or list of strs or set of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_input(name, val=1.0, shape=None, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None, units=None, desc='', tags=None) Add an input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray or Iterable) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if src_indices not provided and val is not an array. Default is None.
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. A value of None implies this input depends on all entries of source. Default is None. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise each entry must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
units (str or None) – Units in which this input variable will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it is unitless.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_output(name, val=1.0, shape=None, units=None, res_units=None, desc='', lower=None, upper=None, ref=1.0, ref0=0.0, res_ref=None, tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
For ExplicitComponent, res_ref defaults to the value in res unless otherwise specified.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if val is not an array. Default is None.
units (str or None) – Units in which the output variables will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it has no units.
res_units (str or None) – Units in which the residuals of this output will be given to the user when requested. Default is None, which means it has no units.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
lower (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – lower bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no lower bound. Default is None.
upper (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – upper bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no upper bound. Default is None.
ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 1. Default is 1.
ref0 (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 0. Default is 0.
res_ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined res_units of this output’s residual when the scaled value is 1. Default is None, which means residual scaling matches output scaling.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs and also when listing results from case recorders.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute_jacvec_product(inputs, d_inputs, d_outputs, mode, discrete_inputs=None) Compute jac-vector product. The model is assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- If mode is:
‘fwd’: d_inputs |-> d_outputs
‘rev’: d_outputs |-> d_inputs
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
d_inputs (Vector) – see inputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_inputs
d_outputs (Vector) – see outputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_outputs
mode (str) – either ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
declare_partials(of, wrt, dependent=True, rows=None, cols=None, val=None, method='exact', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Declare information about this component’s subjacobians.
- Parameters
of (str or list of str) – The name of the residual(s) that derivatives are being computed for. May also contain a glob pattern.
wrt (str or list of str) – The name of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
dependent (bool(True)) – If False, specifies no dependence between the output(s) and the input(s). This is only necessary in the case of a sparse global jacobian, because if ‘dependent=False’ is not specified and declare_partials is not called for a given pair, then a dense matrix of zeros will be allocated in the sparse global jacobian for that pair. In the case of a dense global jacobian it doesn’t matter because the space for a dense subjac will always be allocated for every pair.
rows (ndarray of int or None) – Row indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
cols (ndarray of int or None) – Column indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
val (float or ndarray of float or scipy.sparse) – Value of subjacobian. If rows and cols are not None, this will contain the values found at each (row, col) location in the subjac.
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step, ‘exact’: use the component defined analytic derivatives. Default is ‘exact’.
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
- Returns
Metadata dict for the specified partial(s).
- Return type
dict
-
property
distributed Provide ‘distributed’ property for backwards compatibility.
- Returns
reference to the ‘distributed’ option.
- Return type
bool
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
ode_options= <dymos.ode_options.ODEOptions object>
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_check_partial_options(wrt, method='fd', form=None, step=None, step_calc=None, directional=False) Set options that will be used for checking partial derivatives.
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
method (str) – Method for check: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form for check, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference check. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step_calc (str) – Type of step calculation for check, can be “abs” for absolute (default) or “rel” for relative. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
directional (bool) – Set to True to perform a single directional derivative for each vector variable in the pattern named in wrt.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d.SafeAlt(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
openmdao.core.explicitcomponent.ExplicitComponentSafeAlt class defines the curve representing geographical constraints on the central body surface.
- Other Parameters
num_nodes (int) – Number of nodes where to compute the equations
R (float) – Moon radius [-]
alt_safe (float) – Altitude of the curve representing the geographical constraint [-]
slope (float) – Slope of the curves defining a geographical constraint [-]
-
initialize()[source] Initializes the SafeAlt class variables.
-
setup()[source] Setup of SafeAlt parameters. Declaration of input, output and partials variables.
-
compute(inputs, outputs)[source] Compute the output variables.
-
compute_partials(inputs, jacobian)[source] Compute the partial derivative variables.
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_discrete_input(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add a discrete input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_discrete_output(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
tags (str or list of strs or set of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_input(name, val=1.0, shape=None, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None, units=None, desc='', tags=None) Add an input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray or Iterable) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if src_indices not provided and val is not an array. Default is None.
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. A value of None implies this input depends on all entries of source. Default is None. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise each entry must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
units (str or None) – Units in which this input variable will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it is unitless.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_output(name, val=1.0, shape=None, units=None, res_units=None, desc='', lower=None, upper=None, ref=1.0, ref0=0.0, res_ref=None, tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
For ExplicitComponent, res_ref defaults to the value in res unless otherwise specified.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if val is not an array. Default is None.
units (str or None) – Units in which the output variables will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it has no units.
res_units (str or None) – Units in which the residuals of this output will be given to the user when requested. Default is None, which means it has no units.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
lower (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – lower bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no lower bound. Default is None.
upper (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – upper bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no upper bound. Default is None.
ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 1. Default is 1.
ref0 (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 0. Default is 0.
res_ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined res_units of this output’s residual when the scaled value is 1. Default is None, which means residual scaling matches output scaling.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs and also when listing results from case recorders.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute_jacvec_product(inputs, d_inputs, d_outputs, mode, discrete_inputs=None) Compute jac-vector product. The model is assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- If mode is:
‘fwd’: d_inputs |-> d_outputs
‘rev’: d_outputs |-> d_inputs
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
d_inputs (Vector) – see inputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_inputs
d_outputs (Vector) – see outputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_outputs
mode (str) – either ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
declare_partials(of, wrt, dependent=True, rows=None, cols=None, val=None, method='exact', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Declare information about this component’s subjacobians.
- Parameters
of (str or list of str) – The name of the residual(s) that derivatives are being computed for. May also contain a glob pattern.
wrt (str or list of str) – The name of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
dependent (bool(True)) – If False, specifies no dependence between the output(s) and the input(s). This is only necessary in the case of a sparse global jacobian, because if ‘dependent=False’ is not specified and declare_partials is not called for a given pair, then a dense matrix of zeros will be allocated in the sparse global jacobian for that pair. In the case of a dense global jacobian it doesn’t matter because the space for a dense subjac will always be allocated for every pair.
rows (ndarray of int or None) – Row indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
cols (ndarray of int or None) – Column indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
val (float or ndarray of float or scipy.sparse) – Value of subjacobian. If rows and cols are not None, this will contain the values found at each (row, col) location in the subjac.
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step, ‘exact’: use the component defined analytic derivatives. Default is ‘exact’.
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
- Returns
Metadata dict for the specified partial(s).
- Return type
dict
-
property
distributed Provide ‘distributed’ property for backwards compatibility.
- Returns
reference to the ‘distributed’ option.
- Return type
bool
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_check_partial_options(wrt, method='fd', form=None, step=None, step_calc=None, directional=False) Set options that will be used for checking partial derivatives.
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
method (str) – Method for check: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form for check, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference check. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step_calc (str) – Type of step calculation for check, can be “abs” for absolute (default) or “rel” for relative. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
directional (bool) – Set to True to perform a single directional derivative for each vector variable in the pattern named in wrt.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d.Polar2COE(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
openmdao.core.explicitcomponent.ExplicitComponentPolar2COE class defines the set of equations to derive the Classical Orbital Elements from Polar coordinates.
- Other Parameters
num_nodes (int) – Number of nodes where to compute the equations
GM (float) – Standard gravitational parameter for the central attracting body [-]
-
initialize()[source] Initializes the Polar2COE class variables.
-
setup()[source] Setup of Polar2COE parameters. Declaration of input, output and partials variables.
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_discrete_input(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add a discrete input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_discrete_output(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
tags (str or list of strs or set of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_input(name, val=1.0, shape=None, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None, units=None, desc='', tags=None) Add an input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray or Iterable) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if src_indices not provided and val is not an array. Default is None.
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. A value of None implies this input depends on all entries of source. Default is None. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise each entry must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
units (str or None) – Units in which this input variable will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it is unitless.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_output(name, val=1.0, shape=None, units=None, res_units=None, desc='', lower=None, upper=None, ref=1.0, ref0=0.0, res_ref=None, tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
For ExplicitComponent, res_ref defaults to the value in res unless otherwise specified.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if val is not an array. Default is None.
units (str or None) – Units in which the output variables will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it has no units.
res_units (str or None) – Units in which the residuals of this output will be given to the user when requested. Default is None, which means it has no units.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
lower (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – lower bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no lower bound. Default is None.
upper (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – upper bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no upper bound. Default is None.
ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 1. Default is 1.
ref0 (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 0. Default is 0.
res_ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined res_units of this output’s residual when the scaled value is 1. Default is None, which means residual scaling matches output scaling.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs and also when listing results from case recorders.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute(inputs, outputs, discrete_inputs=None, discrete_outputs=None) Compute outputs given inputs. The model is assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
outputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional output variables read via outputs[key]
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
discrete_outputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete output values.
-
compute_jacvec_product(inputs, d_inputs, d_outputs, mode, discrete_inputs=None) Compute jac-vector product. The model is assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- If mode is:
‘fwd’: d_inputs |-> d_outputs
‘rev’: d_outputs |-> d_inputs
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
d_inputs (Vector) – see inputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_inputs
d_outputs (Vector) – see outputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_outputs
mode (str) – either ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
-
compute_partials(inputs, partials, discrete_inputs=None) Compute sub-jacobian parts. The model is assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
partials (Jacobian) – sub-jac components written to partials[output_name, input_name]
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
declare_partials(of, wrt, dependent=True, rows=None, cols=None, val=None, method='exact', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Declare information about this component’s subjacobians.
- Parameters
of (str or list of str) – The name of the residual(s) that derivatives are being computed for. May also contain a glob pattern.
wrt (str or list of str) – The name of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
dependent (bool(True)) – If False, specifies no dependence between the output(s) and the input(s). This is only necessary in the case of a sparse global jacobian, because if ‘dependent=False’ is not specified and declare_partials is not called for a given pair, then a dense matrix of zeros will be allocated in the sparse global jacobian for that pair. In the case of a dense global jacobian it doesn’t matter because the space for a dense subjac will always be allocated for every pair.
rows (ndarray of int or None) – Row indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
cols (ndarray of int or None) – Column indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
val (float or ndarray of float or scipy.sparse) – Value of subjacobian. If rows and cols are not None, this will contain the values found at each (row, col) location in the subjac.
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step, ‘exact’: use the component defined analytic derivatives. Default is ‘exact’.
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
- Returns
Metadata dict for the specified partial(s).
- Return type
dict
-
property
distributed Provide ‘distributed’ property for backwards compatibility.
- Returns
reference to the ‘distributed’ option.
- Return type
bool
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_check_partial_options(wrt, method='fd', form=None, step=None, step_calc=None, directional=False) Set options that will be used for checking partial derivatives.
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
method (str) – Method for check: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form for check, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference check. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step_calc (str) – Type of step calculation for check, can be “abs” for absolute (default) or “rel” for relative. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
directional (bool) – Set to True to perform a single directional derivative for each vector variable in the pattern named in wrt.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d.Polar2RApo(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
latom.odes.odes_2d.Polar2COEPolar2RApo class defines the set of equations to derive the apoapsis radius from Polar coordinates.
- Other Parameters
ra (float) – Value of the apoapsis radius [-]
-
initialize()[source] Initializes the Polar2RApo class variables.
-
setup()[source] Setup of Polar2RApo parameters. Declaration of input, output and partials variables.
-
compute(inputs, outputs)[source] Compute the output variables.
-
compute_partials(inputs, jacobian)[source] Compute the partial derivative variables.
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_discrete_input(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add a discrete input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_discrete_output(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
tags (str or list of strs or set of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_input(name, val=1.0, shape=None, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None, units=None, desc='', tags=None) Add an input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray or Iterable) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if src_indices not provided and val is not an array. Default is None.
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. A value of None implies this input depends on all entries of source. Default is None. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise each entry must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
units (str or None) – Units in which this input variable will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it is unitless.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_output(name, val=1.0, shape=None, units=None, res_units=None, desc='', lower=None, upper=None, ref=1.0, ref0=0.0, res_ref=None, tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
For ExplicitComponent, res_ref defaults to the value in res unless otherwise specified.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if val is not an array. Default is None.
units (str or None) – Units in which the output variables will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it has no units.
res_units (str or None) – Units in which the residuals of this output will be given to the user when requested. Default is None, which means it has no units.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
lower (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – lower bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no lower bound. Default is None.
upper (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – upper bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no upper bound. Default is None.
ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 1. Default is 1.
ref0 (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 0. Default is 0.
res_ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined res_units of this output’s residual when the scaled value is 1. Default is None, which means residual scaling matches output scaling.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs and also when listing results from case recorders.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute_jacvec_product(inputs, d_inputs, d_outputs, mode, discrete_inputs=None) Compute jac-vector product. The model is assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- If mode is:
‘fwd’: d_inputs |-> d_outputs
‘rev’: d_outputs |-> d_inputs
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
d_inputs (Vector) – see inputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_inputs
d_outputs (Vector) – see outputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_outputs
mode (str) – either ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
declare_partials(of, wrt, dependent=True, rows=None, cols=None, val=None, method='exact', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Declare information about this component’s subjacobians.
- Parameters
of (str or list of str) – The name of the residual(s) that derivatives are being computed for. May also contain a glob pattern.
wrt (str or list of str) – The name of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
dependent (bool(True)) – If False, specifies no dependence between the output(s) and the input(s). This is only necessary in the case of a sparse global jacobian, because if ‘dependent=False’ is not specified and declare_partials is not called for a given pair, then a dense matrix of zeros will be allocated in the sparse global jacobian for that pair. In the case of a dense global jacobian it doesn’t matter because the space for a dense subjac will always be allocated for every pair.
rows (ndarray of int or None) – Row indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
cols (ndarray of int or None) – Column indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
val (float or ndarray of float or scipy.sparse) – Value of subjacobian. If rows and cols are not None, this will contain the values found at each (row, col) location in the subjac.
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step, ‘exact’: use the component defined analytic derivatives. Default is ‘exact’.
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
- Returns
Metadata dict for the specified partial(s).
- Return type
dict
-
property
distributed Provide ‘distributed’ property for backwards compatibility.
- Returns
reference to the ‘distributed’ option.
- Return type
bool
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_check_partial_options(wrt, method='fd', form=None, step=None, step_calc=None, directional=False) Set options that will be used for checking partial derivatives.
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
method (str) – Method for check: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form for check, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference check. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step_calc (str) – Type of step calculation for check, can be “abs” for absolute (default) or “rel” for relative. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
directional (bool) – Set to True to perform a single directional derivative for each vector variable in the pattern named in wrt.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d.Polar2AEH(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
latom.odes.odes_2d.Polar2COEPolar2AEH class defines the set of equations to derive the a and h from Polar coordinates.
The method computes the semi-major axis a, the specific energy and the angular momentum h starting from the polar coordinates r, u, v.
-
setup()[source] Setup of Polar2AEH parameters. Declaration of input, output and partials variables.
-
compute(inputs, outputs)[source] Compute the output variables.
-
compute_partials(inputs, jacobian)[source] Compute the partial derivative variables.
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_discrete_input(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add a discrete input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_discrete_output(name, val, desc='', tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (a picklable object) – The initial value of the variable being added.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
tags (str or list of strs or set of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_input(name, val=1.0, shape=None, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None, units=None, desc='', tags=None) Add an input variable to the component.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray or Iterable) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if src_indices not provided and val is not an array. Default is None.
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. A value of None implies this input depends on all entries of source. Default is None. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise each entry must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
units (str or None) – Units in which this input variable will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it is unitless.
desc (str) – description of the variable
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_output(name, val=1.0, shape=None, units=None, res_units=None, desc='', lower=None, upper=None, ref=1.0, ref0=0.0, res_ref=None, tags=None) Add an output variable to the component.
For ExplicitComponent, res_ref defaults to the value in res unless otherwise specified.
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the variable in this component’s namespace.
val (float or list or tuple or ndarray) – The initial value of the variable being added in user-defined units. Default is 1.0.
shape (int or tuple or list or None) – Shape of this variable, only required if val is not an array. Default is None.
units (str or None) – Units in which the output variables will be provided to the component during execution. Default is None, which means it has no units.
res_units (str or None) – Units in which the residuals of this output will be given to the user when requested. Default is None, which means it has no units.
desc (str) – description of the variable.
lower (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – lower bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no lower bound. Default is None.
upper (float or list or tuple or ndarray or None) – upper bound(s) in user-defined units. It can be (1) a float, (2) an array_like consistent with the shape arg (if given), or (3) an array_like matching the shape of val, if val is array_like. A value of None means this output has no upper bound. Default is None.
ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 1. Default is 1.
ref0 (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined units of this output variable when the scaled value is 0. Default is 0.
res_ref (float) – Scaling parameter. The value in the user-defined res_units of this output’s residual when the scaled value is 1. Default is None, which means residual scaling matches output scaling.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed when calling list_inputs and list_outputs and also when listing results from case recorders.
- Returns
metadata for added variable
- Return type
dict
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute_jacvec_product(inputs, d_inputs, d_outputs, mode, discrete_inputs=None) Compute jac-vector product. The model is assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- If mode is:
‘fwd’: d_inputs |-> d_outputs
‘rev’: d_outputs |-> d_inputs
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
d_inputs (Vector) – see inputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_inputs
d_outputs (Vector) – see outputs; product must be computed only if var_name in d_outputs
mode (str) – either ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
declare_partials(of, wrt, dependent=True, rows=None, cols=None, val=None, method='exact', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Declare information about this component’s subjacobians.
- Parameters
of (str or list of str) – The name of the residual(s) that derivatives are being computed for. May also contain a glob pattern.
wrt (str or list of str) – The name of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
dependent (bool(True)) – If False, specifies no dependence between the output(s) and the input(s). This is only necessary in the case of a sparse global jacobian, because if ‘dependent=False’ is not specified and declare_partials is not called for a given pair, then a dense matrix of zeros will be allocated in the sparse global jacobian for that pair. In the case of a dense global jacobian it doesn’t matter because the space for a dense subjac will always be allocated for every pair.
rows (ndarray of int or None) – Row indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
cols (ndarray of int or None) – Column indices for each nonzero entry. For sparse subjacobians only.
val (float or ndarray of float or scipy.sparse) – Value of subjacobian. If rows and cols are not None, this will contain the values found at each (row, col) location in the subjac.
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step, ‘exact’: use the component defined analytic derivatives. Default is ‘exact’.
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case the approximation method provides its default value.
- Returns
Metadata dict for the specified partial(s).
- Return type
dict
-
property
distributed Provide ‘distributed’ property for backwards compatibility.
- Returns
reference to the ‘distributed’ option.
- Return type
bool
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
initialize() Initializes the Polar2COE class variables.
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_check_partial_options(wrt, method='fd', form=None, step=None, step_calc=None, directional=False) Set options that will be used for checking partial derivatives.
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain the name of any input or output variable. May also contain a glob pattern.
method (str) – Method for check: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form for check, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference check. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step_calc (str) – Type of step calculation for check, can be “abs” for absolute (default) or “rel” for relative. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
directional (bool) – Set to True to perform a single directional derivative for each vector variable in the pattern named in wrt.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.
-
@authors: Alberto FOSSA’ Giuliana Elena MICELI
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d_group.ODE2dVToff(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
openmdao.core.group.GroupODE2dVToff class defines the equations of motion for a two dim. powered trajectory with vertical take-off.
- Other Parameters
time (ndarray) – Represents the time variable of the system [-]
r (ndarray) – Represents a position along the trajectory. The distance is measured from the center of the central body [-]
theta (ndarray) – Angle spawn from the starting point of the orbit to the final one [-]
u (ndarray) – Radial velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
v (ndarray) – Tangential velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
m (ndarray) – Mass of the space vehicle that performs the trajectory [-]
alpha (ndarray) – Angle defining the thrust direction [-]
thrust (ndarray) – Value of the applied thrust force [-]
w (float) – Value of the exhaust velocity [-]
num_nodes (int) – Number of nodes where to compute the equations
GM (float) – Standard gravitational parameter for the central attracting body [-]
R (float) – Moon radius [-]
alt_safe (float) – Altitude of the curve representing the geographical constraint [-]
slope (float) – Slope of the curves defining a geographical constraint [-]
-
initialize()[source] Initializes the ODE2dVToff class variables.
-
setup()[source] Setup of ODE2dVToff parameters. Declaration of subsystem, input and output.
-
add(name, subsys, promotes=None) Add a subsystem (deprecated version of <Group.add_subsystem>).
- Parameters
name (str) – Name of the subsystem being added
subsys (System) – An instantiated, but not-yet-set up system object.
promotes (iter of str, optional) – A list of variable names specifying which subsystem variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. This is for backwards compatibility with older versions of OpenMDAO.
- Returns
The System that was passed in.
- Return type
System
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
add_subsystem(name, subsys, promotes=None, promotes_inputs=None, promotes_outputs=None, min_procs=1, max_procs=None, proc_weight=1.0) Add a subsystem.
- Parameters
name (str) – Name of the subsystem being added
subsys (<System>) – An instantiated, but not-yet-set up system object.
promotes (iter of (str or tuple), optional) – A list of variable names specifying which subsystem variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. If an entry is a tuple of the form (old_name, new_name), this will rename the variable in the parent group.
promotes_inputs (iter of (str or tuple), optional) – A list of input variable names specifying which subsystem input variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. If an entry is a tuple of the form (old_name, new_name), this will rename the variable in the parent group.
promotes_outputs (iter of (str or tuple), optional) – A list of output variable names specifying which subsystem output variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. If an entry is a tuple of the form (old_name, new_name), this will rename the variable in the parent group.
min_procs (int) – Minimum number of MPI processes usable by the subsystem. Defaults to 1.
max_procs (int or None) – Maximum number of MPI processes usable by the subsystem. A value of None (the default) indicates there is no maximum limit.
proc_weight (float) – Weight given to the subsystem when allocating available MPI processes to all subsystems. Default is 1.0.
- Returns
the subsystem that was passed in. This is returned to enable users to instantiate and add a subsystem at the same time, and get the reference back.
- Return type
<System>
-
approx_totals(method='fd', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Approximate derivatives for a Group using the specified approximation method.
- Parameters
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case, the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case, the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case, the approximation method provides its default value.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute_sys_graph(comps_only=False) Compute a dependency graph for subsystems in this group.
Variable connection information is stored in each edge of the system graph.
- Parameters
comps_only (bool (False)) – If True, return a graph of all components within this group or any of its descendants. No sub-groups will be included. Otherwise, a graph containing only direct children (both Components and Groups) of this group will be returned.
- Returns
A directed graph containing names of subsystems and their connections.
- Return type
DiGraph
-
configure() Configure this group to assign children settings.
This method may optionally be overidden by your Group’s method.
You may only use this method to change settings on your children subsystems. This includes setting solvers in cases where you want to override the defaults.
You can assume that the full hierarchy below your level has been instantiated and has already called its own configure methods.
- Available attributes:
name pathname comm options system hieararchy with attribute access
-
connect(src_name, tgt_name, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None) Connect source src_name to target tgt_name in this namespace.
- Parameters
src_name (str) – name of the source variable to connect
tgt_name (str or [str, .. ] or (str, ..)) – name of the target variable(s) to connect
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise it must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
guess_nonlinear(inputs, outputs, residuals, discrete_inputs=None, discrete_outputs=None) Provide initial guess for states.
Override this method to set the initial guess for states.
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
outputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional output variables read via outputs[key]
residuals (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional residuals written to via residuals[key]
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
discrete_outputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete output values.
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
ode_options= <dymos.ode_options.ODEOptions object>
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
set_order(new_order) Specify a new execution order for this system.
- Parameters
new_order (list of str) – List of system names in desired new execution order.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d_group.ODE2dLLO2Apo(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
openmdao.core.group.GroupODE2dLLO2Apo class defines the equations of motion for a two dim. powered trajectory to leave the intial LLO and enter a ballistic arc with apoapsis radius equal to ra.
- Other Parameters
time (ndarray) – Represents the time variable of the system [-]
r (ndarray) – Represents a position along the trajectory. The distance is measured from the center of the central body [-]
theta (ndarray) – Angle spawn from the starting point of the orbit to the final one [-]
u (ndarray) – Radial velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
v (ndarray) – Tangential velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
m (ndarray) – Mass of the space vehicle that performs the trajectory [-]
alpha (ndarray) – Angle defining the thrust direction [-]
thrust (ndarray) – Value of the applied thrust force [-]
w (float) – Value of the exhaust velocity [-]
num_nodes (int) – Number of nodes where to compute the equations
GM (float) – Standard gravitational parameter for the central attracting body [-]
T (float) – Value of the constant thrust force [-]
ra (float) – Value of the apoapsis radius [-]
-
initialize()[source] Initializes the ODE2dLLO2Apo class variables.
-
setup()[source] Setup of ODE2dLLO2Apo parameters. Declaration of subsystem, input and output.
-
add(name, subsys, promotes=None) Add a subsystem (deprecated version of <Group.add_subsystem>).
- Parameters
name (str) – Name of the subsystem being added
subsys (System) – An instantiated, but not-yet-set up system object.
promotes (iter of str, optional) – A list of variable names specifying which subsystem variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. This is for backwards compatibility with older versions of OpenMDAO.
- Returns
The System that was passed in.
- Return type
System
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
add_subsystem(name, subsys, promotes=None, promotes_inputs=None, promotes_outputs=None, min_procs=1, max_procs=None, proc_weight=1.0) Add a subsystem.
- Parameters
name (str) – Name of the subsystem being added
subsys (<System>) – An instantiated, but not-yet-set up system object.
promotes (iter of (str or tuple), optional) – A list of variable names specifying which subsystem variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. If an entry is a tuple of the form (old_name, new_name), this will rename the variable in the parent group.
promotes_inputs (iter of (str or tuple), optional) – A list of input variable names specifying which subsystem input variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. If an entry is a tuple of the form (old_name, new_name), this will rename the variable in the parent group.
promotes_outputs (iter of (str or tuple), optional) – A list of output variable names specifying which subsystem output variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. If an entry is a tuple of the form (old_name, new_name), this will rename the variable in the parent group.
min_procs (int) – Minimum number of MPI processes usable by the subsystem. Defaults to 1.
max_procs (int or None) – Maximum number of MPI processes usable by the subsystem. A value of None (the default) indicates there is no maximum limit.
proc_weight (float) – Weight given to the subsystem when allocating available MPI processes to all subsystems. Default is 1.0.
- Returns
the subsystem that was passed in. This is returned to enable users to instantiate and add a subsystem at the same time, and get the reference back.
- Return type
<System>
-
approx_totals(method='fd', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Approximate derivatives for a Group using the specified approximation method.
- Parameters
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case, the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case, the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case, the approximation method provides its default value.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute_sys_graph(comps_only=False) Compute a dependency graph for subsystems in this group.
Variable connection information is stored in each edge of the system graph.
- Parameters
comps_only (bool (False)) – If True, return a graph of all components within this group or any of its descendants. No sub-groups will be included. Otherwise, a graph containing only direct children (both Components and Groups) of this group will be returned.
- Returns
A directed graph containing names of subsystems and their connections.
- Return type
DiGraph
-
configure() Configure this group to assign children settings.
This method may optionally be overidden by your Group’s method.
You may only use this method to change settings on your children subsystems. This includes setting solvers in cases where you want to override the defaults.
You can assume that the full hierarchy below your level has been instantiated and has already called its own configure methods.
- Available attributes:
name pathname comm options system hieararchy with attribute access
-
connect(src_name, tgt_name, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None) Connect source src_name to target tgt_name in this namespace.
- Parameters
src_name (str) – name of the source variable to connect
tgt_name (str or [str, .. ] or (str, ..)) – name of the target variable(s) to connect
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise it must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
guess_nonlinear(inputs, outputs, residuals, discrete_inputs=None, discrete_outputs=None) Provide initial guess for states.
Override this method to set the initial guess for states.
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
outputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional output variables read via outputs[key]
residuals (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional residuals written to via residuals[key]
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
discrete_outputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete output values.
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
ode_options= <dymos.ode_options.ODEOptions object>
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
set_order(new_order) Specify a new execution order for this system.
- Parameters
new_order (list of str) – List of system names in desired new execution order.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.
-
class
latom.odes.odes_2d_group.ODE2dLLO2HEO(**kwargs)[source] Bases:
openmdao.core.group.GroupODE2dLLO2HEO class defines the equations of motion for a two dim. powered trajectory from LLO to HEO.
- Other Parameters
time (ndarray) – Represents the time variable of the system [-]
r (ndarray) – Represents a position along the trajectory. The distance is measured from the center of the central body [-]
theta (ndarray) – Angle spawn from the starting point of the orbit to the final one [-]
u (ndarray) – Radial velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
v (ndarray) – Tangential velocity of a point along the trajectory [-]
m (ndarray) – Mass of the space vehicle that performs the trajectory [-]
alpha (ndarray) – Angle defining the thrust direction [-]
thrust (ndarray) – Value of the applied thrust force [-]
w (float) – Value of the exhaust velocity [-]
num_nodes (int) – Number of nodes where to compute the equations
GM (float) – Standard gravitational parameter for the central attracting body [-]
T (float) – Value of the constant thrust force [-]
-
initialize()[source] Initializes the ODE2dLLO2HEO class variables.
-
setup()[source] Setup of ODE2dLLO2HEO parameters. Declaration of subsystem, input and output.
-
add(name, subsys, promotes=None) Add a subsystem (deprecated version of <Group.add_subsystem>).
- Parameters
name (str) – Name of the subsystem being added
subsys (System) – An instantiated, but not-yet-set up system object.
promotes (iter of str, optional) – A list of variable names specifying which subsystem variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. This is for backwards compatibility with older versions of OpenMDAO.
- Returns
The System that was passed in.
- Return type
System
-
add_constraint(name, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, adder=None, scaler=None, indices=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a constraint variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (float or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (float or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response. These may be positive or negative integers.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_design_var(name, lower=None, upper=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a design variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the design variable in the system.
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the param
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the param
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of design var that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (iter of int, optional) – If a param is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular design variable. These may be positive or negative integers.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.
-
add_objective(name, ref=None, ref0=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response. This may be a positive or negative integer.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
Notes
The objective can be scaled using scaler and adder, where
\[x_{scaled} = scaler(x + adder)\]or through the use of ref/ref0, which map to scaler and adder through the equations:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}0 = scaler(ref_0 + adder)\\1 = scaler(ref + adder)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]which results in:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}adder = -ref_0\\scaler = \frac{1}{ref + adder}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
-
add_recorder(recorder, recurse=False) Add a recorder to the system.
- Parameters
recorder (<CaseRecorder>) – A recorder instance.
recurse (boolean) – Flag indicating if the recorder should be added to all the subsystems.
-
add_response(name, type_, lower=None, upper=None, equals=None, ref=None, ref0=None, indices=None, index=None, adder=None, scaler=None, linear=False, parallel_deriv_color=None, vectorize_derivs=False, cache_linear_solution=False) Add a response variable to this system.
The response can be scaled using ref and ref0. The argument
ref0represents the physical value when the scaled value is 0. The argumentrefrepresents the physical value when the scaled value is 1.- Parameters
name (string) – Name of the response variable in the system.
type_ (string) – The type of response. Supported values are ‘con’ and ‘obj’
lower (float or ndarray, optional) – Lower boundary for the variable
upper (upper or ndarray, optional) – Upper boundary for the variable
equals (equals or ndarray, optional) – Equality constraint value for the variable
ref (float or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 1.0 in the driver.
ref0 (upper or ndarray, optional) – Value of response variable that scales to 0.0 in the driver.
indices (sequence of int, optional) – If variable is an array, these indicate which entries are of interest for this particular response.
index (int, optional) – If variable is an array, this indicates which entry is of interest for this particular response.
adder (float or ndarray, optional) – Value to add to the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. adder is first in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
scaler (float or ndarray, optional) – value to multiply the model value to get the scaled value for the driver. scaler is second in precedence. adder and scaler are an alterantive to using ref and ref0.
linear (bool) – Set to True if constraint is linear. Default is False.
parallel_deriv_color (string) – If specified, this design var will be grouped for parallel derivative calculations with other variables sharing the same parallel_deriv_color.
vectorize_derivs (bool) – If True, vectorize derivative calculations.
cache_linear_solution (bool) – If True, store the linear solution vectors for this variable so they can be used to start the next linear solution with an initial guess equal to the solution from the previous linear solve.
-
add_subsystem(name, subsys, promotes=None, promotes_inputs=None, promotes_outputs=None, min_procs=1, max_procs=None, proc_weight=1.0) Add a subsystem.
- Parameters
name (str) – Name of the subsystem being added
subsys (<System>) – An instantiated, but not-yet-set up system object.
promotes (iter of (str or tuple), optional) – A list of variable names specifying which subsystem variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. If an entry is a tuple of the form (old_name, new_name), this will rename the variable in the parent group.
promotes_inputs (iter of (str or tuple), optional) – A list of input variable names specifying which subsystem input variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. If an entry is a tuple of the form (old_name, new_name), this will rename the variable in the parent group.
promotes_outputs (iter of (str or tuple), optional) – A list of output variable names specifying which subsystem output variables to ‘promote’ up to this group. If an entry is a tuple of the form (old_name, new_name), this will rename the variable in the parent group.
min_procs (int) – Minimum number of MPI processes usable by the subsystem. Defaults to 1.
max_procs (int or None) – Maximum number of MPI processes usable by the subsystem. A value of None (the default) indicates there is no maximum limit.
proc_weight (float) – Weight given to the subsystem when allocating available MPI processes to all subsystems. Default is 1.0.
- Returns
the subsystem that was passed in. This is returned to enable users to instantiate and add a subsystem at the same time, and get the reference back.
- Return type
<System>
-
approx_totals(method='fd', step=None, form=None, step_calc=None) Approximate derivatives for a Group using the specified approximation method.
- Parameters
method (str) – The type of approximation that should be used. Valid options include: ‘fd’: Finite Difference, ‘cs’: Complex Step
step (float) – Step size for approximation. Defaults to None, in which case, the approximation method provides its default value.
form (string) – Form for finite difference, can be ‘forward’, ‘backward’, or ‘central’. Defaults to None, in which case, the approximation method provides its default value.
step_calc (string) – Step type for finite difference, can be ‘abs’ for absolute’, or ‘rel’ for relative. Defaults to None, in which case, the approximation method provides its default value.
-
check_config(logger) Perform optional error checks.
- Parameters
logger (object) – The object that manages logging output.
-
cleanup() Clean up resources prior to exit.
-
compute_sys_graph(comps_only=False) Compute a dependency graph for subsystems in this group.
Variable connection information is stored in each edge of the system graph.
- Parameters
comps_only (bool (False)) – If True, return a graph of all components within this group or any of its descendants. No sub-groups will be included. Otherwise, a graph containing only direct children (both Components and Groups) of this group will be returned.
- Returns
A directed graph containing names of subsystems and their connections.
- Return type
DiGraph
-
configure() Configure this group to assign children settings.
This method may optionally be overidden by your Group’s method.
You may only use this method to change settings on your children subsystems. This includes setting solvers in cases where you want to override the defaults.
You can assume that the full hierarchy below your level has been instantiated and has already called its own configure methods.
- Available attributes:
name pathname comm options system hieararchy with attribute access
-
connect(src_name, tgt_name, src_indices=None, flat_src_indices=None) Connect source src_name to target tgt_name in this namespace.
- Parameters
src_name (str) – name of the source variable to connect
tgt_name (str or [str, .. ] or (str, ..)) – name of the target variable(s) to connect
src_indices (int or list of ints or tuple of ints or int ndarray or Iterable or None) – The global indices of the source variable to transfer data from. The shapes of the target and src_indices must match, and form of the entries within is determined by the value of ‘flat_src_indices’.
flat_src_indices (bool) – If True, each entry of src_indices is assumed to be an index into the flattened source. Otherwise it must be a tuple or list of size equal to the number of dimensions of the source.
-
declare_coloring(wrt=('*', ), method='fd', form=None, step=None, per_instance=True, num_full_jacs=3, tol=1e-25, orders=None, perturb_size=1e-09, min_improve_pct=5.0, show_summary=True, show_sparsity=False) Set options for deriv coloring of a set of wrt vars matching the given pattern(s).
- Parameters
wrt (str or list of str) – The name or names of the variables that derivatives are taken with respect to. This can contain input names, output names, or glob patterns.
method (str) – Method used to compute derivative: “fd” for finite difference, “cs” for complex step.
form (str) – Finite difference form, can be “forward”, “central”, or “backward”. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
step (float) – Step size for finite difference. Leave undeclared to keep unchanged from previous or default value.
per_instance (bool) – If True, a separate coloring will be generated for each instance of a given class. Otherwise, only one coloring for a given class will be generated and all instances of that class will use it.
num_full_jacs (int) – Number of times to repeat partial jacobian computation when computing sparsity.
tol (float) – Tolerance used to determine if an array entry is nonzero during sparsity determination.
orders (int) – Number of orders above and below the tolerance to check during the tolerance sweep.
perturb_size (float) – Size of input/output perturbation during generation of sparsity.
min_improve_pct (float) – If coloring does not improve (decrease) the number of solves more than the given percentage, coloring will not be used.
show_summary (bool) – If True, display summary information after generating coloring.
show_sparsity (bool) – If True, display sparsity with coloring info after generating coloring.
-
get_approx_coloring_fname() Return the full pathname to a coloring file.
- Parameters
system (System) – The System having its coloring saved or loaded.
- Returns
Full pathname of the coloring file.
- Return type
str
-
get_constraints(recurse=True) Get the Constraint settings from this system.
Retrieve the constraint settings for the current system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all constraints relative to the this system.
- Returns
The constraints defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_design_vars(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the DesignVariable settings from this system.
Retrieve all design variable settings from the system and, if recurse is True, all of its subsystems.
- Parameters
recurse (bool) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all design vars relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each design variable.
- Returns
The design variables defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
get_linear_vectors(vec_name='linear') Return the linear inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Parameters
vec_name (str) – Name of the linear right-hand-side vector. The default is ‘linear’.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals linear vectors for vec_name.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_nonlinear_vectors() Return the inputs, outputs, and residuals vectors.
- Returns
(inputs, outputs, residuals) – Yields the inputs, outputs, and residuals nonlinear vectors.
- Return type
tuple of <Vector> instances
-
get_objectives(recurse=True) Get the Objective settings from this system.
Retrieve all objectives settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all objective relative to the this system.
- Returns
The objectives defined in the current system.
- Return type
dict
-
get_responses(recurse=True, get_sizes=True) Get the response variable settings from this system.
Retrieve all response variable settings from the system as a dict, keyed by variable name.
- Parameters
recurse (bool, optional) – If True, recurse through the subsystems and return the path of all responses relative to the this system.
get_sizes (bool, optional) – If True, compute the size of each response.
- Returns
The responses defined in the current system and, if recurse=True, its subsystems.
- Return type
dict
-
guess_nonlinear(inputs, outputs, residuals, discrete_inputs=None, discrete_outputs=None) Provide initial guess for states.
Override this method to set the initial guess for states.
- Parameters
inputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional input variables read via inputs[key]
outputs (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional output variables read via outputs[key]
residuals (Vector) – unscaled, dimensional residuals written to via residuals[key]
discrete_inputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete input values.
discrete_outputs (dict or None) – If not None, dict containing discrete output values.
-
is_active() Determine if the system is active on this rank.
- Returns
If running under MPI, returns True if this System has a valid communicator. Always returns True if not running under MPI.
- Return type
bool
-
property
linear_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
list_inputs(values=True, prom_name=False, units=False, shape=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of input names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return input values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only inputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like object) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of input names and other optional information about those inputs
- Return type
list
-
list_outputs(explicit=True, implicit=True, values=True, prom_name=False, residuals=False, residuals_tol=None, units=False, shape=False, bounds=False, scaling=False, hierarchical=True, print_arrays=False, tags=None, includes=None, excludes=None, out_stream=<object object>) Return and optionally log a list of output names and other optional information.
If the model is parallel, only the local variables are returned to the process. Also optionally logs the information to a user defined output stream. If the model is parallel, the rank 0 process logs information about all variables across all processes.
- Parameters
explicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from explicit components. Default is True.
implicit (bool, optional) – include outputs from implicit components. Default is True.
values (bool, optional) – When True, display/return output values. Default is True.
prom_name (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the promoted name of the variable. Default is False.
residuals (bool, optional) – When True, display/return residual values. Default is False.
residuals_tol (float, optional) – If set, limits the output of list_outputs to only variables where the norm of the resids array is greater than the given ‘residuals_tol’. Default is None.
units (bool, optional) – When True, display/return units. Default is False.
shape (bool, optional) – When True, display/return the shape of the value. Default is False.
bounds (bool, optional) – When True, display/return bounds (lower and upper). Default is False.
scaling (bool, optional) – When True, display/return scaling (ref, ref0, and res_ref). Default is False.
hierarchical (bool, optional) – When True, human readable output shows variables in hierarchical format.
print_arrays (bool, optional) – When False, in the columnar display, just display norm of any ndarrays with size > 1. The norm is surrounded by vertical bars to indicate that it is a norm. When True, also display full values of the ndarray below the row. Format is affected by the values set with numpy.set_printoptions Default is False.
tags (str or list of strs) – User defined tags that can be used to filter what gets listed. Only outputs with the given tags will be listed. Default is None, which means there will be no filtering based on tags.
includes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to include in the check. Default is None, which includes all components in the model.
excludes (None or list_like) – List of glob patterns for pathnames to exclude from the check. Default is None, which excludes nothing.
out_stream (file-like) – Where to send human readable output. Default is sys.stdout. Set to None to suppress.
- Returns
list of output names and other optional information about those outputs
- Return type
list
-
property
ln_solver Get the linear solver for this system.
-
property
metadata Get the options for this System.
-
property
msginfo Our instance pathname, if available, or our class name. For use in error messages.
- Returns
Either our instance pathname or class name.
- Return type
str
-
property
nl_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
property
nonlinear_solver Get the nonlinear solver for this system.
-
ode_options= <dymos.ode_options.ODEOptions object>
-
reconfigure() Perform reconfiguration.
- Returns
If True, reconfiguration is to be performed.
- Return type
bool
-
record_iteration() Record an iteration of the current System.
-
resetup(setup_mode='full') Public wrapper for _setup that reconfigures after an initial setup has been performed.
- Parameters
setup_mode (str) – Must be one of ‘full’, ‘reconf’, or ‘update’.
-
run_apply_linear(vec_names, mode, scope_out=None, scope_in=None) Compute jac-vec product.
This calls _apply_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
scope_out (set or None) – Set of absolute output names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
scope_in (set or None) – Set of absolute input names in the scope of this mat-vec product. If None, all are in the scope.
-
run_apply_nonlinear() Compute residuals.
This calls _apply_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
run_linearize(sub_do_ln=True) Compute jacobian / factorization.
This calls _linearize, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
sub_do_ln (boolean) – Flag indicating if the children should call linearize on their linear solvers.
-
run_solve_linear(vec_names, mode) Apply inverse jac product.
This calls _solve_linear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
- Parameters
vec_names ([str, ..]) – list of names of the right-hand-side vectors.
mode (str) – ‘fwd’ or ‘rev’.
-
run_solve_nonlinear() Compute outputs.
This calls _solve_nonlinear, but with the model assumed to be in an unscaled state.
-
set_initial_values() Set all input and output variables to their declared initial values.
-
set_order(new_order) Specify a new execution order for this system.
- Parameters
new_order (list of str) – List of system names in desired new execution order.
-
system_iter(include_self=False, recurse=True, typ=None) Yield a generator of local subsystems of this system.
- Parameters
include_self (bool) – If True, include this system in the iteration.
recurse (bool) – If True, iterate over the whole tree under this system.
typ (type) – If not None, only yield Systems that match that are instances of the given type.
-
use_fixed_coloring(coloring=<object object>, recurse=True) Use a precomputed coloring for this System.
- Parameters
coloring (str) – A coloring filename. If no arg is passed, filename will be determined automatically.
recurse (bool) – If True, set fixed coloring in all subsystems that declare a coloring. Ignored if a specific coloring is passed in.